Table of Contents
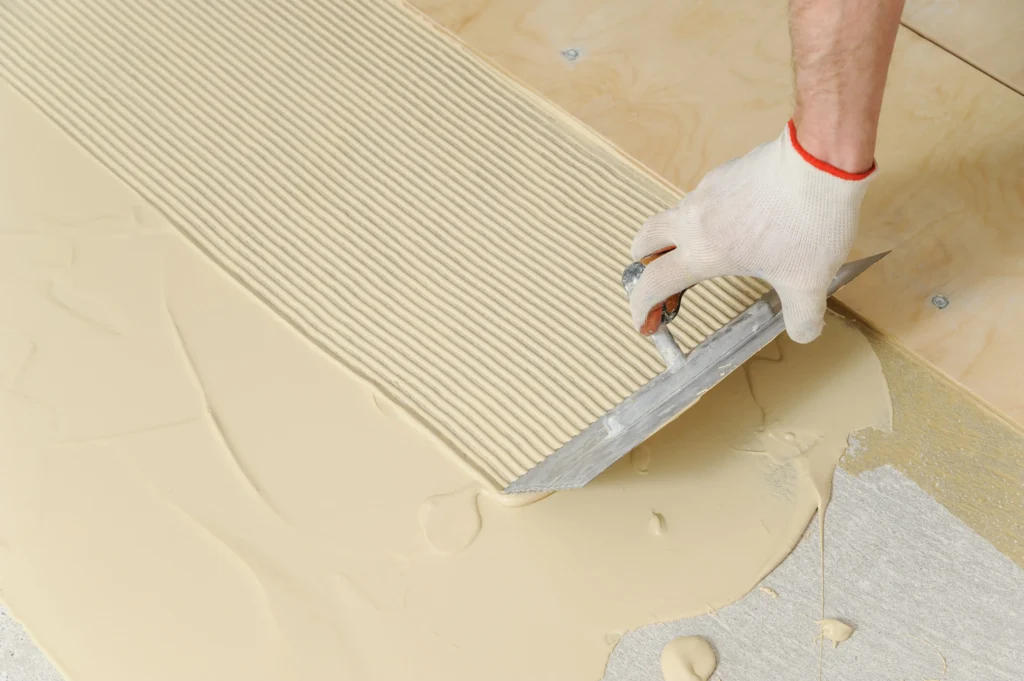
What is a C1 Tile Adhesive?

What is a C1 Tile Adhesive Formulation?
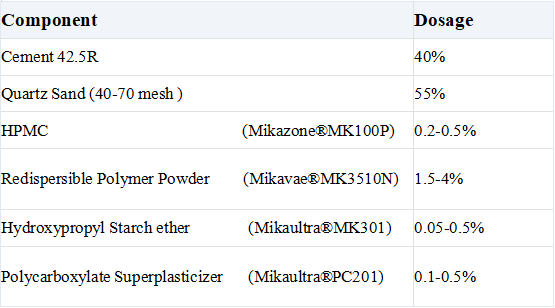
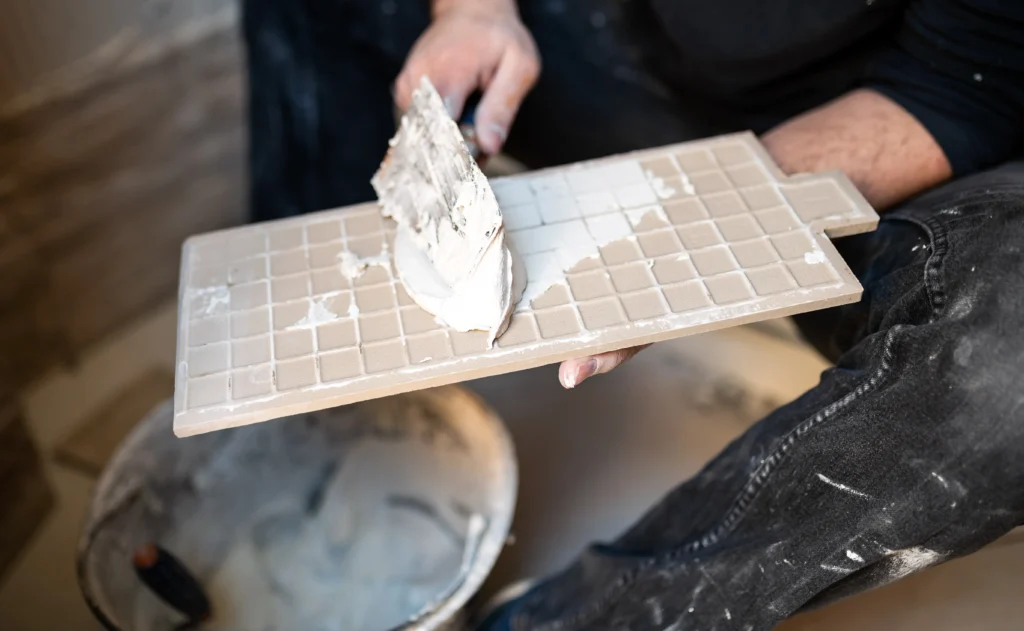
Main components of C1 tile adhesive formulations
2.1 Cement
2.2 Sand
2.3 Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC)

2.3.1 Benefits of HPMC in C1 Tile Adhesive
Improved Workability: HPMC enhances the open time and smooth application of C1 tile adhesive, ensuring better spreadability and reducing sagging on vertical surfaces for precise tile placement.
Water Retention: HPMC slows water evaporation, allowing proper cement hydration and strong bond formation, even in dry or high-temperature conditions, preventing premature drying and weak adhesion.
Enhanced Adhesion Strength: By improving cohesion and reducing shrinkage, HPMC boosts the adhesive’s bonding performance, ensuring durable tile installation with minimal risk of delamination or cracking over time.
Excellent Thickening: HPMC provides excellent viscosity control, preventing tile slippage after application and maintaining consistent mortar thickness, crucial for large-format or heavy tiles in C1 adhesives.
2.3.2 Typical Dosage & Selection Criteria of HPMC in C1 Tile Adhesive
- Desired viscosity & workability.
- Substrate absorbency (higher dosages for porous surfaces).
- Climate conditions (hot/dry climates need more HPMC for water retention).
- Viscosity Grades:
- Low viscosity (e.g., 40,000–60,000 mPa·s): Balances workability and sag resistance.
- High viscosity (>100,000 mPa·s): For superior anti-sag, but may reduce workability.
- Particle Size: Fine powders (e.g., 80–100 mesh) dissolve faster, avoiding lumps.
2.3.3 Common Issues & Solutions about HPMC in C1 Tile Adhesive Formulations
Poor Water Retention:
HPMC fails to retain sufficient water, leading to premature drying and weak adhesion.
Solutions:
Use higher viscosity HPMC (e.g., 150,000–200,000 mPa·s)
Adjust cellulose ether dosage (0.2–0.5%)
Add a small amount of retarder (e.g.Mikaultra®MK301 starch ethers)
Slow Dissolution & Lumps Formation
HPMC clumps when mixed, causing uneven dispersion and reduced workability.
Solutions:
Pre-mix HPMC with other dry powders (e.g., cement, sand) before adding water
Use surface-treated HPMC (e.g., instant-dissolving grades)
Gradually sprinkle HPMC into water while stirring
2.4 Redispersible Polymer Powder(RDP)

2.4.1 Benefits of Redispersible Polymer Powder in C1 Tile Adhesives
- Crack Resistance: RDP improves the adhesive’s elasticity, reducing stress from thermal or structural movement and preventing cracks in tiles or grout lines for long-term durability.
- Superior Adhesion Strength: RDP forms a polymer film that boosts bonding to tiles and substrates, even on low-absorbency surfaces like porcelain, ensuring strong and reliable adhesion in C1 adhesives.
- Improved Water Resistance: RDP-modified adhesives resist moisture penetration, protecting the bond from weakening in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens while maintaining breathability to prevent trapped moisture.
- Enhanced Workability: RDP enhances mortar consistency, reducing sagging and improving open time for easier tile adjustment, while ensuring uniform application and strong cohesion in vertical applications.
2.4.2 Formulation Design Guidelines for Redispersible Polymer Powder(RDP) in C1 Tile Adhesive
- Dosage Optimization
- Typical Range: 1.5–4% by weight of dry mix.
- Low Dosage (1.5–2.5%): Balances cost and performance for standard applications.
- High Dosage (3–4%): Required for high-flexibility adhesives or extreme conditions (e.g., exterior tiles, heated floors).
- Polymer Type Selection
- VAE (Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene): Most common for C1 adhesives, offering balanced adhesion, flexibility, and cost.
- Acrylic or Styrene-Acrylic: Higher water resistance and UV stability, suitable for exterior applications.
- Tg (Glass Transition Temperature) Considerations: Lower Tg polymers (e.g., -10°C to +10°C) enhance flexibility in cold climates.
- Synergy with Key Additives
- HPMC: Combines HPMC’s water retention with RDP’s adhesion to optimize open time and bond strength.
- Superplasticizers: RDP compensates for reduced cohesion caused by superplasticizers, maintaining anti-sag properties.
2.5 Hydroxypropyl Starch Ether
2.5.1 Benefits of Starch Ether in C1 Tile Adhesives
- Improved Workability: Starch ether enhances the spreadability and plasticity of C1 tile adhesives, ensuring easy troweling and better coverage for efficient tile installation.
- Excellent Water Retention: It slows water evaporation, maintaining optimal moisture for cement hydration, which improves bond strength and prevents premature drying in hot or dry conditions.
- Anti-Sagging: Starch ether provides viscosity control, reducing tile slippage on vertical surfaces and ensuring consistent mortar thickness for secure placement of large or heavy tiles.
- Cost-Effective Performance: As a natural polymer, starch ether offers a balance of adhesion, workability, and water retention at a lower cost compared to synthetic alternatives in C1 adhesives
2.5.2 Typical Dosage in C1 Tile Adhesives
- Standard dosage: 0.05–0.3% (by weight of dry powder mix).
- Higher dosages (up to 0.5%) may be used for enhanced anti-slip properties.
- Desired Workability – Higher amounts improve smooth application.
- Open Time Requirements – Adjusts water retention for longer working times.
- Anti-Slip Performance – Increased dosage reduces tile movement.
- Compatibility with Other Additives – Must balance with cellulose ethers (HPMC/MHEC).
2.6 Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer
2.6.1 Benefits of Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer in C1 Tile Adhesives
- Superior Water Reduction: PCE significantly lowers water demand while enhancing flowability, ensuring easier application and improved spreadability of C1 tile adhesives without compromising strength.
- High Early Strength: PCE optimizes cement hydration, accelerating early strength development and delivering superior final bond strength for faster installation and long-term durability in demanding conditions.
- Excellent Sag Resistance: PCE provides precise rheology control, preventing tile slippage on vertical surfaces and ensuring consistent mortar thickness for secure bonding of large-format or heavy tiles.
- Enhanced Durability: PCE-modified adhesives exhibit reduced shrinkage and improved flexibility, minimizing micro-cracks and enhancing long-term performance under thermal or mechanical stress.

